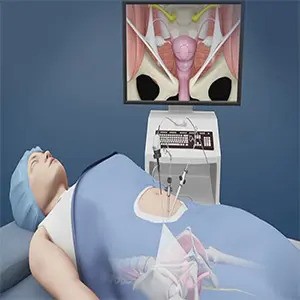
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Overview
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to remove a woman’s uterus (womb) through small incisions in the abdomen using a laparoscope—a thin tube with a camera and light. In some cases, the ovaries and fallopian tubes may also be removed, depending on the underlying medical condition and patient preferences.
A specific type, called laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy (LSH), involves removing the uterus while preserving the cervix, the lower part of the uterus.
After undergoing a hysterectomy, a woman will no longer menstruate and cannot become pregnant.
Indications for Hysterectomy
Your doctor may recommend laparoscopic hysterectomy for the following conditions:
- Uterine fibroids
- Endometriosis that hasn’t improved with medical or prior surgical treatment
- Uterine prolapse (uterus descends into the vagina)
- Cancer of the uterus, cervix, or ovaries
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding unresponsive to other treatments
- Chronic pelvic pain affecting quality of life
Pre-Surgical Evaluation
Before surgery, your doctor may conduct several diagnostic tests, including:
- Pelvic ultrasound: To evaluate the uterus and ovaries using high-frequency sound waves
- Pap smear: To detect precancerous or cancerous cervical cells
- Endometrial biopsy: Sampling of the uterine lining to detect abnormal or cancerous changes
Surgical Procedure
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered.
- Incisions: 3–4 small incisions are made in the abdomen, often near the belly button.
- Laparoscope insertion: A camera-equipped laparoscope is introduced to view internal organs on a monitor.
- Tissue dissection: Surgical instruments detach the uterus from surrounding tissues and ligaments.
- Uterus removal: The uterus is removed in sections through the small incisions. The cervix is preserved in LSH.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Ovaries and fallopian tubes may be removed or retained, depending on age, condition, and patient consent.
Benefits of Laparoscopic (Minimally Invasive) Hysterectomy
- Smaller incisions and less visible scarring
- Reduced pain after surgery
- Lower risk of infection
- Faster recovery and shorter hospital stay
- Minimal blood loss
- Most cases performed as day-care (outpatient) surgery
Postoperative Care
Recovery depends on the type of hysterectomy and the patient's healing progress. Key post-op guidelines include:
- Pain medications and antibiotics will be prescribed.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects or strenuous activity.
- Resume light activities once discomfort and bleeding subside.
- Sexual activity may be resumed after 6 weeks (upon doctor’s advice).
- Avoid exercise or abdominal strain for at least 3 weeks post-surgery.
Possible Risks and Complications
Although rare, risks associated with laparoscopic hysterectomy include:
- Infection or bleeding
- Blood clots
- Bladder or ureter injury
- Urinary incontinence
- Vaginal prolapse
- Painful intercourse
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Early menopause if ovaries are removed
When to Contact Your Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Heavy vaginal bleeding
- Fever above 101°F (38.3°C)
- Severe abdominal pain
- Redness, swelling, or discharge at the incision site
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Shortness of breath